femoral torsion positive test|craig's test femoral anteversion : member club Femoral Anteversion is a common congenital condition caused by intrauterine positioning which lead to increased anteversion of the femoral neck relative to the femur with compensatory internal rotation of the femur. . WEB118K Followers, 3,075 Following, 6,720 Posts
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Simulador de Apostas - Mega-Sena, Quina, Lotofácil, Timemania, Dupla-Sena, Lotomania, Dia de Sorte, Super-Sete, +Milionária, PowerBall, Mega Millions e Euromillions.
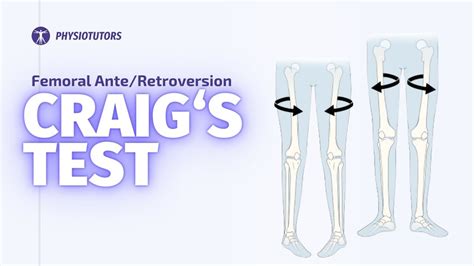
Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence . See more Femoral Anteversion is a common congenital condition caused by intrauterine positioning which lead to increased anteversion of the femoral neck relative to the femur with compensatory internal rotation of the femur. .
Femoral neck anteversion (FNA) is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur. Differences in FNA affect the biomechanics of the . Femoral Anteversion test (Craig’s test) Clinical examination Musculoskeletal system Orthopedics. Last modified: Jun 27, 2020. Synonym: Trochanteric prominence angle test. Patient position: Prone with knee on test .
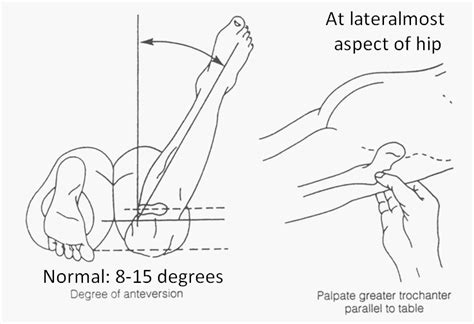
Craig's Test. Purpose: To determine the anteversion of the femur. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The tested limb's knee is placed in 90 degrees of flexion.Positive Test: If measures femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. Interpretation: Decreases with age from about 30 0 at birth to about 8 0 to 15 0 at adulthood. . Decreased femoral anteversion was associated with out-toeing gait, whereas increased femoral anteversion was associated with in-toeing gait. Decreased femoral version also was associated with increased incidence of . Femoral torsion is measured between top line connecting femoral head center, determined by perfectly fitting circle, to center of femoral neck base directly superior to lesser trochanter and bottom line connecting posterior .
Radiographic features. Femoral anteversion can be determined by measuring the angle formed between the long axis of the femoral neck and a line parallel to the dorsal aspect of the .
Positive Finding: A positive Craig’s test occurs when hip internal rotation is 15˚ or greater, indicating femoral anteversion. Normal hip anteversion is 8 to 15 degrees.
Purpose: To determine the anteversion of the femur. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The tested limb's knee is placed in 90 degrees of flexion. The examiner rotates the hip medially and laterally, while palpating the greater . Inguinal or femoral hernia Testicular torsion Varicocele Associated with the hip . MRI has a sensitivity of 91%, specificity of 92%, positive predictive value of 95%, and negative predictive .Meanwhile, the femoral nerve may also be stressed by this test. It is recommended to test both sides if the patient complains of pain bilaterally. Importantly, at least three positive signs of the SIJ provocation tests are required before a possible diagnosis of SIJ pathology. . Positive Likelihood Ratio (LR+) –The ratio of a positive test . Fig. 1A —28-year-old woman with 2-year history of right-sided groin pain and positive anterior impingement test (pain with hip flexion, adduction, and internal rotation). Case emphasizes importance of appropriate imaging workup of patients with suspected femoroacetabular impingement to arrive at correct diagnosis. . Femoral torsion should .
Foot progression angle measurements will have positive values with out-toeing and negative values with intoeing. 4, 5 Evaluation of hip rotation shows increased internal rotation with femoral . Femoral antetorsion is the angle between the femoral neck and the femoral condyles and was first described by Julius Wolff in 1868 [1–3].Abnormal femoral antetorsion is associated with slipped capital femoral epiphysis, developmental dysplasia of the hip, and early-onset hip osteoarthritis [4–6].Recently, it has been shown that abnormal femoral antetorsion . Femoral anteversion (also called hip anteversion) is when the knee is excessively twisted inward relative to the hip. Learn about diagnosis and treatment. . such as external tibial torsion – an outward rotation of the tibia (shinbone). This type of complex case is called "tetra-torsional malalignment,” which has sometimes also been called . Background Assessment of femoral torsion at preoperative hip imaging is commonly recommended. However, it is unclear whether MRI is as accurate as CT and how different methods affect femoral torsion measurements. Purpose To compare MRI- and CT-based assessment of femoral torsion by using four commonly used measurement methods in .
Find me here: https://linktr.ee/thephysiochannelFREE ONLINE COURSE (for therapists): Mastering Frozen Shoulder: https://daniel-lawrence-fc31.mykajabi.com/off.The patella sits within the femoral groove; the fascies articularis patellae (posterior side) is covered with cartilage that glides over the cartilage of the anterior part of the femoral condyles (femoral groove). . Cook et al suggest a positive diagnosis of patellofemoral pain syndrome when: . Muscle length-Modified Thomas test to assess .Femoral anteversion is self-correcting in up to 99 percent of cases, and the long-term outlook is very positive for most children with the condition. Femoral anteversion doesn't typically lead to arthritis or any other future health problems. The outlook is also excellent for children with a severe form of the condition who need surgery.
If only one test or 2 other tests are positive, further testing is required to obtain a valid result. [13] The posterior pelvic pain provocation test has a high intertester reliability of 94,1 (kappa=0,64-0,82 and p<0,001) and a high degree of sensitivity (80-88%) and specificity (100%) in 2 studies of moderate to high methodological quality. Ischiofemoral impingement (IFI) is a cause of hip pain in young adults due to a mechanical conflict between the proximal femur and ischium, initially described between the lesser trochanter and ischial tuberosity [].It is more common in women and is bilateral in one third of cases [2, 3].Patients usually present with hip and buttock pain and a positive posterior .Femoral anteversion is a condition in which the femoral neck leans forward with respect to the rest of the femur. . To protect your loved one, please do not visit if you are sick or have a COVID-19 positive test result. Get more resources on masking and COVID-19 precautions. Vaccines ; Masking Guidelines; Visitor Guidelines ; Close. Search .
The anatomical morphology of the femoral neck plays an important role in the recognition and treatment of diseases around the hip joint. Many morphological parameters (the femoral neck-shaft angle, femoral neck anteversion angle (FNAA), and so on) are closely related to the findings in clinical studies [1,2,3,4,5,6].However, Kate suggested that femoral neck .The Craig’s test is used to identify femoral anteversion, which is a term used to describe the relative rotation between the femoral shaft and the femoral neck. . How to Interpret Craig’s Test. Positive Finding: A positive Craig’s test occurs when hip internal rotation is 15˚ or greater, indicating femoral anteversion. Normal hip .
femoral anteversion test procedure
femoral anteversion test criteria
Femoral neck anteversion is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur1. Multiple publications describe the etiology, epidemiology, causalgia, diagnostic imaging, .
Which of the following describes the hips having an angle of torsion greater than 20 degrees? a. Retroverted b. Coxa Valgus c . Which statement is true of the femoral triangle? a. The lymph nodes are located . What would a positive hip scouring test indicate? a. Osteochondral defect of the femur b. Tight rectus femoris c. Femoral acetabular .The diagnostic value of 2 positive tests of the 4 selected test was as follows: Values (95% CI) Sensitivity 0.88 (0.64, 0.97) Specificity 0.78 (0.61, 0.89) . Levangie P. Four clinical tests of sacroiliac joint dysfunction: the association of test results with innominate torsion among patients with and without low back pain. Phys Ther. 1999;79 .
femoral anteversion pdf
The positive result of the test indicates Piriformis syndrome. Although the pain could be because of both the piriformis muscle and a lumbar disc herniation which can be identified by performing the Straight Leg Raising Test. The Freiburg sign also stretches the piriformis muscle where, in the supine lying position, the hip is passively .
femoral anteversion normal range
The Craig test (or Femoral Anteversion test) is used to assess anteversion/ retroversion of the femoral neck.. How do you do the Craig Test? The patient is positioned in prone with the knee flexed to 90 degrees. The clinician rotates the hip through the full ranges of hip internal and external rotation, while palpating the greater trochanter and determining the .Craig's test is a passive test used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. The examiner palpates the greater trochanter and rotates the hip internally and . Background Torsional deformities of the femur include femoral retrotorsion and increased femoral torsion, which are possible causes for hip pain and osteoarthritis. In patients with aberrant femoral torsion, the femoral neck axis has a smaller than normal anteversion angle . The test was positive if the patient was unable to accomplish the posture and ultimately fell backward. In a passive squatting test, the patient lay on the examination table and the examiner brought the flexed knee close to the .
Measuring femoral torsion with the trochanteric prominence angle test: With the patient prone, anteversion is measured when the greater trochanteric is palpated in its most prominent position as the hip is internally and externally rotated. When the greater trochanter is most prominent, the femoral neck is horizontal.
femoral anteversion in children
The etiology of intoeing (i.e., metatarsus adductus, internal tibial torsion, and increased femoral anteversion) is debated, although the causes generally can be correlated with the patient's age .Prone Knee Bending Test | Reversed Lasègue Test | Femoral Nerve Test The diagnosis of lumbar radicular syndrome is commonly made by patient-history alone and additional testing to confirm this hypothesis is often not necessary. 90% of cases involve nerve roots L4-L5 or L5-S1, as those segments are exposed to the highest static and kinetic forces.
WEBInaugurado em 1990, o Pesqueiro João Hara conta com. Pesqueiro João Hara, Cotia, Sao Paulo, Brazil. 2,498 likes · 35 talking about this · 504 were here. Inaugurado em 1990, o Pesqueiro João Hara conta com três lagos com diversas opções de peixes.
femoral torsion positive test|craig's test femoral anteversion